- Usage in publication:
-
- Hinton formation*
- Modifications:
-
- Named
- Dominant lithology:
-
- Shale
- Sandstone
- Limestone
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
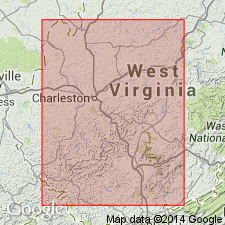
Summary:
Named Hinton formation for Hinton, Summers Co., WV. Consists of heterogeneous mass of variegated shales, sandstones of varying character, and impure limestones, ranging in thickness from 1050 to 1100 feet. Lowest bed is heavy sandstone, which is prominent feature along railroad from Hinton to Sandstone. The Hinton underlies the Princeton conglomerate and is of Mississippian age.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Hinton Formation*
- Modifications:
-
- Revised
- Areal extent
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
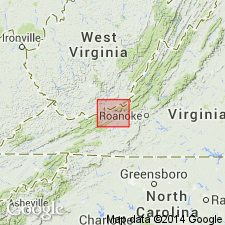
Summary:
Use of Mauch Chunk Group extended into Giles Co., VA, and bordering areas of Mercer, Summer, and Monroe Cos., WV. Mauch Chunk Group is divided into ascending Bluefield Formation, Hinton Formation, Princeton Sandstone, and Bluestone Formation.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Hinton Formation
- Modifications:
-
- Revised
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
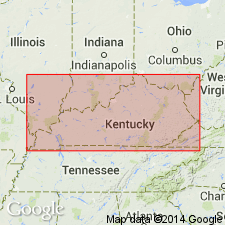
Summary:
Pennington Group in study area is divided into (ascending) Bluefield Formation, Hinton Formation, Princeton Sandstone, and Bluestone Formation, which are "informally projected" into KY according to the author. Hinton is composed predominantly of red and green shales with interbedded limestones and sandstones. Stony Gap Sandstone Member ("Maxon sand" of drillers) at the base varies from siliceous to calcareous sandstone. Little Stone Gap Member near the top of the Hinton is an argillaceous limestone or calcareous shale. The Hinton reaches a maximum of 260 m. Age is Late Mississippian.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Hinton Formation*
- Modifications:
-
- Overview
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
Summary:
Pennington Formation is approximately equivalent to Hinton and Bluefield Formations. Lower unnamed member of Pennington is approximately equivalent to Stony Gap Sandstone Member of Hinton and lower part of upper unnamed member of Pennington is approximately equivalent to Little Stone Gap Member of Hinton elsewhere in Appalachian basin.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Hinton Formation
- Modifications:
-
- Areal extent
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
Summary:
Hinton Formation crops out from Cumberland Gap northeastward to Bluefield, WV, along the southeast edge of the Appalachian Plateaus. Formation has a maximum thickness of about 1100 ft in Tazewell Co. and thins to the northwest and west across Buchanan Co. to about 200 ft along the VA-KY border. Southwest of the Russell Fork fault, in the subsurface, the Hinton ranges between 400 and 700 ft. Unit is composed of interbedded gray, grayish-red, and greenish-gray shale and siltstone with minor amounts of calcareous siltstone and limestone. Divided into seven distinct lithologic members: the Stony Gap Sandstone Member, the middle red member, the Little Stone Gap Member, the middle shale member, the Tallery Sandstone Member, the Pratter Shale Member, and the upper shale member. Overlies the Bluefield Formation and underlies the Bluestone Formation. Age is Late Mississippian (Chesterian).
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
For more information, please contact Nancy Stamm, Geologic Names Committee Secretary.
Asterisk (*) indicates published by U.S. Geological Survey authors.
"No current usage" (†) implies that a name has been abandoned or has fallen into disuse. Former usage and, if known, replacement name given in parentheses ( ).
Slash (/) indicates name conflicts with nomenclatural guidelines (CSN, 1933; ACSN, 1961, 1970; NACSN, 1983, 2005, 2021). May be explained within brackets ([ ]).

