- Usage in publication:
-
- Greenbrier Formation
- Modifications:
-
- Revised
- Overview
- Dominant lithology:
-
- Limestone
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
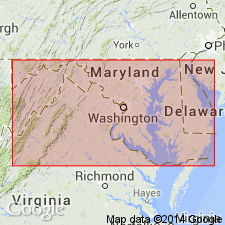
Summary:
Author retains name Greenbrier because it is entrenched in the literature, but Greenbrier of MD is similar to WV Greenbrier Group only in that it is a marine carbonate. Unit thins northward from its type area where it is 1800 ft to 250 to 125 ft in western MD. Greenbrier is here revised in western MD to include (ascending) Loyalhanna, Deer Valley, Savage Dam (new name), and Wymps Gap Members.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Greenbrier Limestone
- Modifications:
-
- Overview
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
Summary:
Lower unnamed member of Newman Limestone is also known as Greenbrier Limestone elsewhere in the Appalachian basin.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Greenbrier Limestone*
- Modifications:
-
- Biostratigraphic dating
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
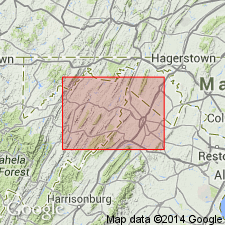
Summary:
Conodont biostratigraphy indicates that the Greenbrier Limestone is of Late Mississippian (Chesterian) age. Conodonts indicative of Chesterian faunas were recovered from the Loyalhanna Limestone Member and the Wymps Gap Member.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Greenbrier Limestone
- Modifications:
-
- Overview
- Areal extent
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
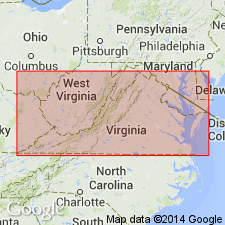
Summary:
In report area, Greenbrier Limestone crops out from Cumberland Gap northeastward along the northwest flank of the Powell Valley anticline to Little Stone Gap where the formation curves around the nose of the anticline. In outcrop reaches a maximum thickness of 850 ft in Tazewell and Russell Cos. and in the subsurface thins northwestward to about 200 ft near the Buchanan Co., VA, and Pike Co., KY, border. Consists of a thick sequence of dark-gray to brownish-gray to very light gray, micritic to sparry, highly fossiliferous oolitic, locally cherty limestone with interbedded shale, siltstone, and argillaceous limestone. Lower 40 ft contains black, gray, and pale-red chert nodules. A pale-brown dolomite occurs near the top of the chert-bearing zone. Bedding is thick near the base and thin near the top. Unit is divided into the (ascending) Little Valley Limestone Member, the St. Louis Limestone Member (Hillsdale Member of Reger, 1926), the "St. Genevieve" Limestone Member, and the Gasper Limestone Member. [Subdivisions are discussed in text but are not shown in figures.] Disconformably overlies the Maccrady Shale or the Price Formation and gradationally underlies the Bluefield Formation. Age is Late Mississippian (Meramecian and Chesterian).
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
For more information, please contact Nancy Stamm, Geologic Names Committee Secretary.
Asterisk (*) indicates published by U.S. Geological Survey authors.
"No current usage" (†) implies that a name has been abandoned or has fallen into disuse. Former usage and, if known, replacement name given in parentheses ( ).
Slash (/) indicates name conflicts with nomenclatural guidelines (CSN, 1933; ACSN, 1961, 1970; NACSN, 1983, 2005, 2021). May be explained within brackets ([ ]).

