- Usage in publication:
-
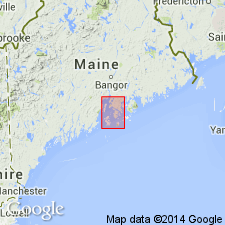
- Penobscot formation*
- Modifications:
-
- Named
- Dominant lithology:
-
- Slate
- Schist
- Quartzite
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- New England province
Summary:
Named the Penobscot formation for Penobscot Bay, central-south ME. Consists of metamorphosed shaly sediments (slates, schists, quartzites) typically developed along nearly whole length of western shore of Penobscot Bay. Color varies from light gray through steel gray and purplish gray to black, the darker grays being predominant. Locally injected and metamorphosed by granite and diorite. Weathered surfaces usually rusty. In a few places only the rock exhibits a very perfect slaty cleavage, highly inclined to bedding planes. Conformably overlies Battie quartzite. The Penobscot is of Cambrian(?) age.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
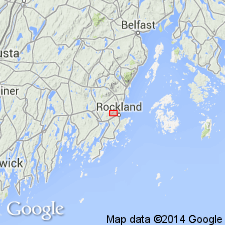
- Penobscot Formation
- Modifications:
-
- Age modified
- Geochronologic dating
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- New England province
Summary:
The age of the Penobscot Formation in ME is changed to Ordovician based on Rb-Sr date of 460+\-10 Ma.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
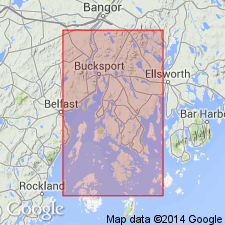
- Penobscot Formation*
- Modifications:
-
- Overview
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- New England province
Summary:
Penobscot Formation in northern Penobscot Bay, ME consists of rusty-weathering, black or gray iron sulfide-rich schist with beds of pelite, graded silty sands, and rare limestone and calcareous sandstone beds. Proportion of black pelitic beds increases from 50 percent to about 75 percent in inferred upper part of formation. Locally middle-amphibolite facies rocks have been retrograded to biotite-muscovite-chlorite schist. Contains injected zone of complexly intruded dikes of diorite and muscovite granite. Lower part contains Gushee Member consisting of biotite-bearing amphibolite. Penobscot correlates with Ordovician Cookson Group of Fyffe and Riva (1990, Revised stratigraphy of the Cookson Group of southwestern New Brunswick and adjacent Maine: Atlantic Geology, v. 26, no. 3, p. 271-275), Ludman (1991, Revised stratigraphy of the Cookson Group in eastern Maine and southwestern New Brunswick, an alternative view: Atlantic Geology, v. 27, no. 1, p. 49-55), and West and others (1992, Silurian age for the Pocomoonshine Gabbro-Diorite, southeastern Maine and its regional tectonic implications: American Journal of Science, v. 292, p. 253-272). Penobscot is intruded by granite of Northport, dated at 430 Ma (Early Silurian; Ericksson and others, 1989) and by Spruce Head pluton, dated at 440+/-5 Ma (R.E. Zartman, 1991, written commun.). Ordovician(?).
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
For more information, please contact Nancy Stamm, Geologic Names Committee Secretary.
Asterisk (*) indicates published by U.S. Geological Survey authors.
"No current usage" (†) implies that a name has been abandoned or has fallen into disuse. Former usage and, if known, replacement name given in parentheses ( ).
Slash (/) indicates name conflicts with nomenclatural guidelines (CSN, 1933; ACSN, 1961, 1970; NACSN, 1983, 2005, 2021). May be explained within brackets ([ ]).

