- Usage in publication:
-
- Ludlowville shales
- Modifications:
-
- Named
- Dominant lithology:
-
- Shale
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
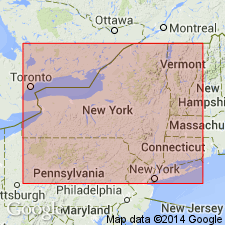
Summary:
Named Ludlowville shales in the Hamilton group for Ludlowville, Tompkins Co., NY. Consists of bluish or olive shale with different fossils from those of the underlying olive shale [Skaneateles shale]. Underlies Encrinal limestone. The Ludlowville is of Middle Devonian age.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Ludlowville Formation
- Modifications:
-
- Revised
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
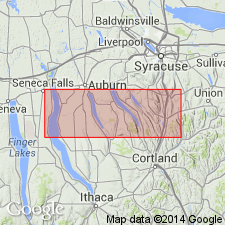
Summary:
Peppermill Gulf bed is a newly recognized, fossil-rich horizon at the base of the Centerfield Member (and the correlative "Chenango facies") of the Ludlowville Formation. Overlies the Levanna Member of the Skaneateles Formation. Bed consists of a bioturbated, silty mudstone with a diverse assemblage of brachiopods, bivalves, and some rugose corals. Outcrops extend from Big Hollow Creek on the west side of Cayuga Lake to Case Hill Ravine south of Syracuse. Age is Middle Devonian.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Ludlowville Formation
- Modifications:
-
- Revised
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
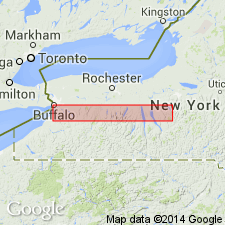
Summary:
Ledyard Member of Ludlowville Formation is subdivided into newly named Winspear and overlying Elma submembers in west-central NY. The Winspear encompasses the lower 15 m of the Ledyard and includes the Alden pyrite beds and the Athol Springs limestone bed, which marks its top. The Elma encompasses the upper 10 to 12 m of the Ledyard and includes the Bullis trilobite beds and the Pond Brook interval, which includes the Mt. Vernon bed at its top. The Ledyard overlies the Centerfield Limestone Member and underlies the Spring Brook Submember of the Wanakah Member.
["Submember" not recognized as a formal stratigraphic rank term (CSN, 1933; ACSN, 1961, 1970; NACSN, 1983, 2005). Considered informal until formally published. The rank or lithologic term should not be capitalized.]
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Ludlowville Shale*
- Modifications:
-
- Areal extent
- Revised
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
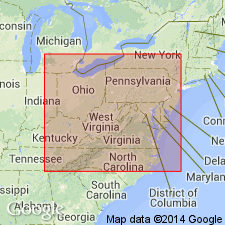
Summary:
Ludlowville Shale of Hamilton Group extended from southwestern NY, into western PA and eastern OH and into subsurface in northern WV and westernmost MD (Garrett Co.). Revised from Formation to Ludlowville Shale.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Ludlowville Formation
- Modifications:
-
- Overview
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
Summary:
The Ludlowville Formation of western NY has been subdivided since 1930 into four members: the Centerfield Limestone (4-14 m), the Ledyard Shale (10-30 m), the Wanakah Member (12-21 m), and the Jaycox Member (<1-18 m). In central NY, the Ludlowville consists mainly of variably silty mudstones with lesser proportions of fossiliferous siltstone and sandstone. It was subdivided by Smith (1935) above the Centerfield into the Otisco Shale (50 m), the Ivy Point Siltstone (20 m), the Spafford Shale (8 m) and the Owasco Siltstone (<1-2.5 m). Recent studies have been made to correlate these units precisely. The Otisco Shale has been correlated with the black Ledyard Shale, and the Ivy Point with parts of the Wanakah Member. The Spafford and the Owasco are not so easily equated with the post-Wanakah of western NY. The Spafford was not recognized west of Owasco Lake until recently though it had been traced eastward to the Chenango Valley. The Spafford is now known to extend westward into the Cayuga and Seneca Lake region as a sparsely fossiliferous siliciclastic mudstone. It extends still farther west as a thin tongue of shale, formerly assigned to the Wanakah. It is bounded at the base by the Limerick Road Bed (new) and at the top by the Hills Gulch Bed of the Jaycox. The Jaycox extends from Syracuse westward to Elma. It is underlain by the Wanakah Member from Erie Co. eastward to East Bethany. From Genesee Co. eastward, mudstones, here assigned to the Spafford Member, are interposed between the Wanakah and the base of the Hills Gulch Bed of the Jaycox. The Owasco Siltstone Member of central NY correlates with the Hills Gulch Bed of the Jaycox of western NY.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Ludlowville Formation*
- Modifications:
-
- Overview
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
Summary:
Author follows usage of Baird (1979). Ludlowville Formation shows Wanakah Shale Member underlying Jaycox Shale Member. Age is Middle Devonian.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
For more information, please contact Nancy Stamm, Geologic Names Committee Secretary.
Asterisk (*) indicates published by U.S. Geological Survey authors.
"No current usage" (†) implies that a name has been abandoned or has fallen into disuse. Former usage and, if known, replacement name given in parentheses ( ).
Slash (/) indicates name conflicts with nomenclatural guidelines (CSN, 1933; ACSN, 1961, 1970; NACSN, 1983, 2005, 2021). May be explained within brackets ([ ]).

