- Usage in publication:
-
- Indian Bluff group
- Modifications:
-
- Original reference
- Dominant lithology:
-
- Sandstone
- Shale
- Coal
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
Summary:
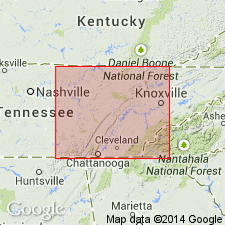
Pg. 1, 6, pls. 2, 3, 4. Indian Bluff group. Includes strata between top of Slatestone group (new) and base of Graves Gap group (new). Thickness at type section 455 feet; in southwestern part of Cumberland Mountains 300 to 470 feet; thins northwestward; on Cumberland Block, 150 to 200 feet. Includes (ascending) shale interval, Seeber Flats sandstone (new), shale interval, Stockstill sandstone (new), shale interval, Indian Fork sandstone (new), shale interval, and Pioneer sandstone. Indian Fork sandstone not present at type locality. Age is Early Pennsylvanian (Pottsville).
Type section: Cross Mountain, Lake City quadrangle, eastern TN. Named from Indian Bluff on eastern edge of Braden Flats, a short distance northeast of Graves Gap, Anderson Co., eastern TN. Section begins at top of Jellico coal on Militia Hill and ends on top of Pioneer sandstone upon which Mountain View Church is located.
Source: US geologic names lexicon (USGS Bull. 1200, p. 1862).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Indian Bluff Formation
- Modifications:
-
- [Revised]
- Mapped
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
Summary:
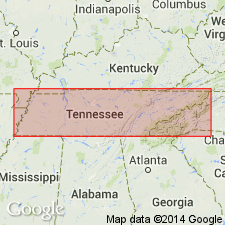
(East-central and East sheets.) Indian Bluff Formation. Shale, sandstone, siltstone, and thin coal beds; from Pioneer Sandstone Member to Jellico coal. Thickness 150 to 415 feet in east-central Tennessee; 150 to 250 feet in eastern Tennessee. Lies below Graves Gap Formation and above Slatestone Formation. Age is Pennsylvanian.
[The Indian Bluff Group of Wilson and others (1956) is reduced to formation rank. Its constituent formations, the Pioneer, Indian Fork, Stockstill, and Seeber Flats, are also reduced in rank to members (only the Pioneer is incl. on State geol. map). See also under Graves Gap and Slatestone.]
Source: Publication.
- Usage in publication:
-
- Indian Bluff Formation
- Modifications:
-
- Overview
- Dominant lithology:
-
- Shale
- Sandstone
- Siltstone
- Coal
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
Summary:
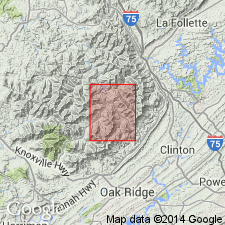
Consists of clayey to sandy, light-brown to dark-gray shale with coal beds and minor intercalated sandstone and siltstone; and yellowish-gray to yellowish-brown, fine- to medium-grained, thin-to thick-bedded sandstone, cross-bedded in part. Base of formation at top of Jellico coal bed.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Indian Bluff Formation*
- Modifications:
-
- Revised
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
Summary:
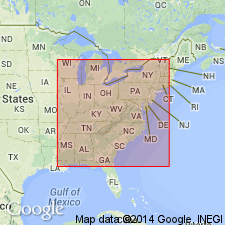
Indian Bluff Formation is used in TN. Includes Seeber Flats, Stockstill, Indian Fork, and Pioneer Sandstone Members. Includes part of strata previously assigned to Jellico Formation (abandoned herein); Pioneer Sandstone member reassigned from Jellico to Indian Bluff.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
For more information, please contact Nancy Stamm, Geologic Names Committee Secretary.
Asterisk (*) indicates published by U.S. Geological Survey authors.
"No current usage" (†) implies that a name has been abandoned or has fallen into disuse. Former usage and, if known, replacement name given in parentheses ( ).
Slash (/) indicates name conflicts with nomenclatural guidelines (CSN, 1933; ACSN, 1961, 1970; NACSN, 1983, 2005, 2021). May be explained within brackets ([ ]).

