- Usage in publication:
-
- Andreas red beds
- Modifications:
-
- Named
- Dominant lithology:
-
- Sandstone
- Shale
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
Summary:
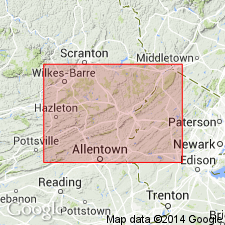
Pg. 1142, 1143, 1144. Andreas red beds in Keyser formation. Name provisionally proposed for red sandstone forming ledges above the quarry face at Andreas and Snyders, in Schuylkill County, eastern Pennsylvania. Provisionally placed in Keyser formation. Consists of red sandstone and shale. Thickness 17.5 feet at type locality. Age unknown but overlies beds bearing Keyser fauna [authors consider Keyser to be Silurian or Devonian age] and is overlain by loose fragments of chert bearing a New Scotland fauna in the road north of Snyders. Report includes correlation chart, measured sections [Andreas red beds not measured].
Type locality: quarry of William Loch 0.5 mi southeast of Andreas, on east side of small stream, and about 0.25 mi northeast of quarry of J. Rudolph, (Hamburg quadrangle) Schuylkill Co., PA. [Upper and lower boundary concealed.] Origin of name not stated by author, but probably named for the town of Andreas.
Source: US geologic names lexicon (USGS Bull. 1350, p. 25-26); GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Andreas Red Beds*
- Modifications:
-
- Revised
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
Summary:
Used as Andreas Red Beds of Swartz and Swartz (1941) and given formation rank. Described in the area of Blue Mountain and Cherry, Chestnut, and Stony Ridges, Pennsylvania. Consists of red, green, and gray, pebbly sandstone, siltstone, and shale. Northeasternmost outcrop is approximately 1.5 miles west of Bowmanstown, Pennsylvania. Overlain by either New Scotland Formation or Shriver Chert. Underlain by Decker Formation. Possible nonmarine correlative of Coeymans Formation. Thickness from 0 to 50 feet. Age is Late Silurian or Early Devonian.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Andreas Red Beds*
- Modifications:
-
- Revised
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
Summary:
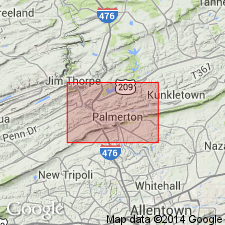
Used as Andreas Red Beds of Swartz and Swartz (1941) of the Decker Formation [called Keyser by Swartz and Swartz]. No fossils found. Age is latest Silurian or Early Devonian. It may be bounded above and below by unconformities and be correlative to rocks to the east in the Delaware Water Gap area, such as the Rondout or Coeymans Formations.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Andreas Red Beds*
- Modifications:
-
- Revised
- Overview
- Reference
- Dominant lithology:
-
- Sandstone
- Siltstone
- Shale
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Appalachian basin
Summary:
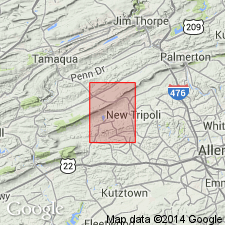
Removed from the Decker Formation and given formation rank. Reference section established in active quarry 3700 ft (1130 m) due south from town of Andreas, PA, where formation is completely exposed. Detailed lithology is as follows: Grayish-red, dusky red to moderate reddish brown, and lesser light-gray to pinkish gray, laminated to thin-bedded (beds as much as 1.5 ft (0.5 m) thick), lenticular shale, siltstone, and fine- to coarse-grained sandstone. Slightly conglomeratic in places with quartz pebbles as much as 0.5 in. (1.3 cm) long, and with minor shale-chip conglomerate. Weathers dark yellowish-orange to light-brown. Planar bedded, cross bedded, rippled, burrow mottled. Some channels. Contains ostracodes and a pelecypod not useful in constraining age. Correlates with either Coeymans Formation or upper part of the Decker Formation. 65 ft (20 m) thick.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Reston GNULEX).
For more information, please contact Nancy Stamm, Geologic Names Committee Secretary.
Asterisk (*) indicates published by U.S. Geological Survey authors.
"No current usage" (†) implies that a name has been abandoned or has fallen into disuse. Former usage and, if known, replacement name given in parentheses ( ).
Slash (/) indicates name conflicts with nomenclatural guidelines (CSN, 1933; ACSN, 1961, 1970; NACSN, 1983, 2005, 2021). May be explained within brackets ([ ]).

