- Usage in publication:
-
- Goble volcanic series*
- Modifications:
-
- Named
- Biostratigraphic dating
- Dominant lithology:
-
- Basalt
- Pyroclastics
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Cascades province
- Oregon-Washington Coast Ranges province
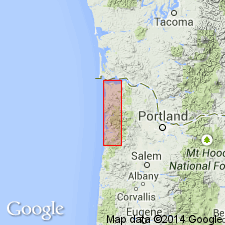
Summary:
Named for town of Goble, OR, in St. Helens 15' quad on Columbia River. Description of series prepared by W.D. Lowry and E.M. Baldwin [see Wilkinson and others, 1946, Oregon Dept. of Geol. and Min. Industries Bull. 31]. Excellent exposures are near Goble, as well as along both sides of Columbia River especially between Woodland and Kelso, WA, along U.S. HWY 99, where measured section more than 5000 ft. Composed of basaltic flows, pyroclastic rocks, and minor sedimentary rocks. Basal part interbedded with tuffaceous sedimentary deposits that contain Cowlitz (upper Eocene fauna). Overlain unconformably by strata that contain a fauna of Pittsburg Bluff (Oligocene) or slightly older age. Assigned late Eocene and Oligocene(?) age.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Menlo GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Goble volcanic member
- Modifications:
-
- Revised
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Oregon-Washington Coast Ranges province
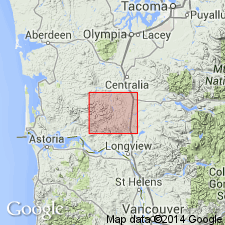
Summary:
Since Goble Volcanics is relatively thin in lower Cowlitz River-eastern Willapa Hills area and interfingered with Cowlitz formation it is considered justifiable to lower the rank of Goble volcanics to "Goble volcanics member" of Cowlitz formation in this area. "Goble volcanics" constitutes a much thicker unit of formational rank in another area.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Menlo GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Goble Volcanics
- Modifications:
-
- Revised
- Age modified
- Biostratigraphic dating
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Cascades province
- Oregon-Washington Coast Ranges province
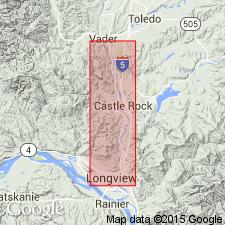
Summary:
"Goble Volcanic Series" renamed "Goble Volcanics," in accordance with article 9f of the Code of Stratigraphic Nomenclature [ACSN, 1961]. Historical overview is included. Lists of megafossils and foraminifers with localities identified by E.M. Baldwin and W.W. Rau respectively, included in report. Age is considered to be late Eocene to early Oligocene, on basis of fossils found in interbeds near base and top of Goble Volcanics.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Menlo GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Goble Volcanics*
- Modifications:
-
- Age modified
- Revised
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Cascades province
- Oregon-Washington Coast Ranges province
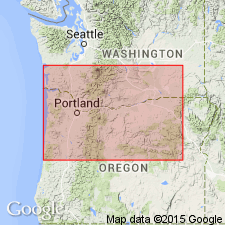
Summary:
"Upper Eocene volcanic sequences also compose ... the Goble Volcanics ... along the Columbia River about 45 miles north of Portland." p.50 [Rank is therefore lowered from series to formation.]
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Menlo GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Goble Volcanic Series
- Modifications:
-
- Geochronologic dating
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Cascades province
- Oregon-Washington Coast Ranges province
Summary:
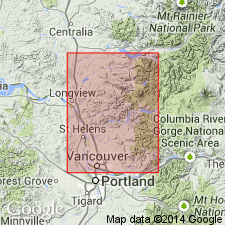
Whole rock K-Ar ages (provided by R.A. Duncan of Oregon State University) are as follows: 35.9 +/-0.4 Ma and 32.2 +/-0.3 Ma (early Oligocene) collected from 19 km east of Interstate 5 on WA HWY 504 along Toutle River; 45.0 +/-1.4 Ma and 41.4 +/-1.3 Ma (late Eocene) from 19 km east of interstate 5 along Coweman River. This confirms age based on fossil assemblages within interfingering units of Goble Volcanic Series.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Menlo GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Goble Volcanics*
- Modifications:
-
- Areal extent
- Geochronologic dating
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Oregon-Washington Coast Ranges province
Summary:
[Mapped in fig.2 in belt about 30 mi long, averaging about 5 mi wide, parallel to and 5 to 10 mi north of Columbia River, northwest of Kelso, WA, and northwest of previously described exposures.] Unconformably overlies middle Eocene Crescent Formation. Is late Eocene in age. Two K-Ar ages from basalt flows reported as 39 and 32 Ma; (R.E. Wells, M.J. Heatherington and R.W. Tabor, unpublished data, 1980); older age more compatible with microfossil ages as given by Armentrout (1981).
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Menlo GNULEX).
- Usage in publication:
-
- Goble Volcanics*
- Modifications:
-
- Age modified
- AAPG geologic province:
-
- Cascades province
- Oregon-Washington Coast Ranges province
Summary:
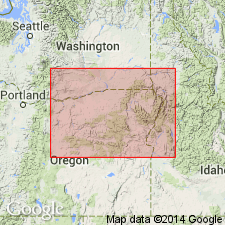
Age of Goble Volcanics is late Eocene and early Oligocene based on studies by Livingston (1966) and Beck and Burr (1979) [which are based on stratigraphic relations to units containing fossils and K-Ar ages ranging from 45.0 +/-1.4 Ma to 32.2 +/-0.3 Ma.
Source: GNU records (USGS DDS-6; Menlo GNULEX).
For more information, please contact Nancy Stamm, Geologic Names Committee Secretary.
Asterisk (*) indicates published by U.S. Geological Survey authors.
"No current usage" (†) implies that a name has been abandoned or has fallen into disuse. Former usage and, if known, replacement name given in parentheses ( ).
Slash (/) indicates name conflicts with nomenclatural guidelines (CSN, 1933; ACSN, 1961, 1970; NACSN, 1983, 2005, 2021). May be explained within brackets ([ ]).

